Difference Between 2g 3g 4g

3G and 4G can be differentiated concerning technology compliance, data transfer rate, capacity, IP architecture and number of connections, etc. 3G stands for 3rd generation in which optimized mobile are developed for enabling data and broadband services with better connectivity. 4G LTE stands for 4th generation which delivers more capacity for quicker and improvised mobile broadband experiences and allowing more connections.
The third generation of mobile communication technology, or 3G, is the successor to the 2G and 1G standards. A download made using a 3G network should expect speeds of 600Kbps to 1.4Mbps, according to Sprint. A 3G phone will work in an area with 4G coverage, but will only connect at 3G speeds, and likewise a 4G phone will work in an area with 2G, but only connect at 2G speeds. It's just like if you compared a Ferrari to a Model T first in a residential neighborhood, and then on a racetrack.
'Z Series Innovations' is an e-learning solution for learning all technical stuff online. It is an online portal that gives an enhanced way of learning and guidance in various fields of engineering which include robotics, electronics, communication,computer science, embedded systems and its real life applications.
3G and 4G technology are associated with mobile communication standards. Mobile Communications is one of the constantly developing areas to deliver faster and better mobile broadband experiences. Each new technology offers the significant advancement in performance and capabilities compared to its predecessor. It provides the ability to access the internet over different devices like tab, laptop, desktop and mobile phones.
Content: 3G Technology Vs 4G Technology
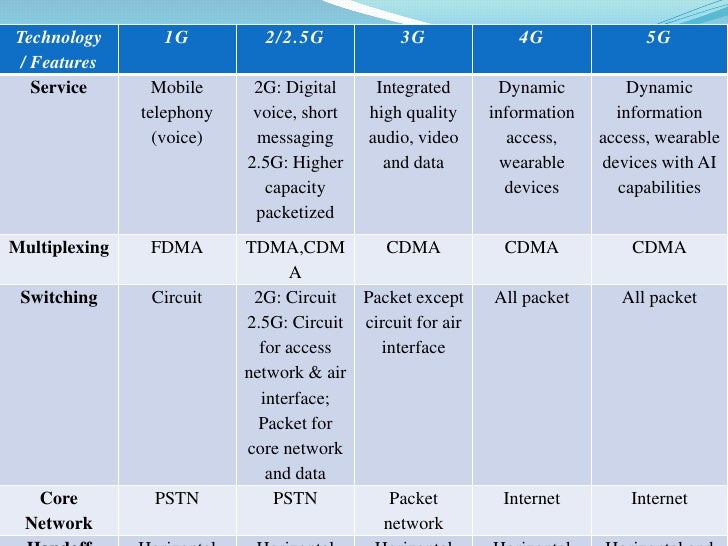
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | 3G Technology | 4G Technology |
|---|---|---|
| Data Bandwidth | 2 Mbps - 21 Mbps | 2 Mbps - 1 Gbps |
| Peak Upload Rate | 5 Mbps | 500 Mbps |
| Peak Download Rate | 21 Mbps | 1 Gbps |
| Switching Technique | Packet Switching | Packet Switching, Message Switching |
| Standards | IMT 2000 3.5G HSDPA 3.75G HSUPA | Single Unified standard Wimax and LTE |
| Technology Stack | Digital Broadband Packet Data CDMA 2000, UMTS, EDGE etc. | Digital Broadband Packet Data Wimax2 and LTE Advances. |
| Frequency Band | 1.8 – 2.5 GHz | 2 – 8 GHz |
| Network Architecture | Wide Area Cell Based | Integration of Wireless LAN and Wide Area |
| Forward Error Correction | 3G uses turbo codes for error correction. | Concatenated codes are used for error correction in 4G. |
| Handoff | Horizontal | Horizontal and Vertical |
Definition of 3G Technology
3G is a generation of standards for mobile telecommunication services that satisfies the International Mobile Telecommunications -2000 (IMT-2000) provides the ability to transfer voice and data (music downloads, emails and instant messaging) over the same network simultaneously.
It delivers broadband capacity, supports larger number of voice and data customers of lower incremental cost than its predecessor 2G. 3G uses Circuit switching for voice communication, and Packet switching for Data Communication.
Maximum data transfer rates supported by 3G:
- 2.05 Mbits/second for stationary devices.
- 384 Kbits/second for devices moving at a slow pace.
- 128 Kbits/second for devices moving at high speed.
FORMATION OF 3GPP
3GPP (3rd Generation Partnership Project) was evolved during formation of governing bodies which included the collaboration of both GSM and UMTS. 3GPP was working under observation of ITU-R (International Telecommunication Union-radiocommunication sector) one of the sectors of ITU.
It is responsible for managing the international radio frequency spectrum, to ensure the efficient use of spectrum and defines technology families, associates specific parts of the spectrum with the families.
ITU finally ratified a family of five 3G standards which are part of the 3G framework known as IMT-2000, after trying to build a single 3G standard:
- Three standards based on CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access), namely:
- CDMA2000
- WCDMA (Wideband Code Division Multiple Access)/HSPA+ (High-Speed Packet Access)
- TDSCDMA.
- Two standards based on based on TDMA(Time Division Multiple Access), namely:
- FDMA/TDMA
- TDMA-SC(EDGE).
Definition of 4G Technology
4G stands for 4th Generation Technology, and it is a venture to develop, incorporate the current 2G (2nd Generation), 3G (3rd Generation), WLAN (Wireless Local Area Network), short-range, fixed wire systems into a single and broadcast, entirely functional, consistent and coherent internetwork.
It is an extension of 3G technology which provides capabilities defined by ITU (International Telecommunications Union) in IMT (International Mobile Telecommunications) includes features like scalability, flexibility, efficiency, self-governance, security to support interfacing with different types of networks and a multitude of new and existing services.
It offers completely converged customised services (voice, data and multimedia) at data rates of up to 100 Mbps and pervasive mobile access for:
- High-resolution mobile television
- IP telephony
- Gaming services
- Video conferencing
- 3D television
The enhanced versions of current technologies cover GSM, GPRS, CDMA, IMT-2000, W-CDMA, CDMAone, Wireless LANs and Bluetooth are integrated into 4G. The high-quality audio/video streaming over end to end Internet Protocol is expected.
Difference Between 2g 3g 4g And Lte
Versions of Mobile LTE (Long Term Evolution) and WiMAX (Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access) in unison support much less than 1 Gbit/s peak bit rate, are branded 4G by service providers, but there is no complete IMT-Advanced compliance.
The main goal of 4G LTE was to achieve high mobility and global connectivity.
The IP Core network is developed further to support high data rates, advanced application services and management of IP and radio network more efficiently and has much more exacting requirements.
The spread spectrum radio technology which was used in 3G is replaced by:
- OFDMA (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access) multi-carrier transmission.
- FDE (Frequency-Domain Equalization) stratagem.
As a result, it transfers very high bit rates without being affected by immense multipath radio propagation.
For MIMO (Multiple-Input Multiple-Output) communications, peak bit rate is further enhanced by using smart antenna arrays. Higher order modulation up to 64 QAM and MBMS (Multimedia Broadcast Multicast services) for broadcasting is used.
Key Differences Between 3G and 4G Technology
The points covered below presents the difference between 3G and 4G technology:
- When it comes to data bandwidth 3G provides 21 Mbps and 4G offers 1 Gbps maximum data bandwidth.
- The maximum uploading rate of 3G is 5 Mbps whereas 500 Mbps is the highest uploading rate of 4G.
- The highest download rate of 3G is 21 Mbps. As against 4G offers 1Gbps peak download rate.
- 3G uses packet switching for data transmission. On the other hand, both packet and message switching are used in 4G.
- In 4G, Hybrid network architecture is used. Conversely, 3G uses wide area cell based network.
- CDMA is employed in 3G. As against, 4G utilises OFDMA (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access).
- Handoff management is done vertically in 3G, but in 4G it’s done vertically as well as horizontally.
- Full IP based Network is supported in 4G. However, in case of 3G, it is circuit and packet based.
3G/UMTS Architecture
The Constituent parts of 3G UMTS network are
• Mobile Station: It could be anything like data and voice-enabled mobile phones, tabs or computers which could be used as an end user.
• RAN (Radio Access Network): It consists of base stations and radio access controller which bridges the gap between Mobile Station and Core Network. It also controls and manages the air interface for the whole network.
• CN (Core Network): It provides the main processing and management of subsystems. The 3G UMTS network Architecture is migrated from GSM with some enhancements in core network elements.
The core network is classified into two parts i.e. Circuit Switched Domain and Packet-switched domain.
- Circuit Switched Domain: It uses Circuit Switched Network in which dedicated link or channel is provided for a particular time slot to set of users. The two blocks shown in Circuit Switched Domain are:
- MSC – Mobile Switching Centre manages circuit switched calls.
- GMSC – Gateway MSC acts as an intermediary between external and internal networks.
- Packet-switched domain: It uses IP Network where IP’s are responsible for transmitting and receiving data among two or more devices. The two blocks shown in Packet Switched Domain are:
- SGSN(Serving GPRS Support Node): The various functions provided by SGSN are mobility management, session management, billing, communication with other areas of the network.
- GGSN(Gateway GPRS Support Node): It can be considered as a very complex router and handles the internal operations between the external packet switched networks and UMTS packet switched network.

- IMS(IP Multimedia Subsystem): It is an Architectural framework which supplies IP multimedia services.
4G LTE Architecture
The Constituent parts of 4G LTE network are
- User Equipment (UE): It could be any device capable of establishing communication functions like mobile phones, tabs, computers, etc.
- Evolved UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access Network (E-UTRAN): It controls radio communication between user equipment and EPC. LTE mobile can connect with just one cell and one base station at a time. Main operations performed by EBS(Evolved Base Station)
- Analog and digital processing functions of LTE air interface are used to transmit and receive radio transmission to all the LTE-enabled devices.
- Handles low-level operation by sending the signalling messages and commands.
- Evolved Packet Core (EPC): It communicates with internal and external packet data networks and IP multimedia subsystem. It consists of following blocks:
- HSS: Home Subscriber Server holds all the information about all the network operator’s subscribers in a central database.
- MME: Mobility Management Entity handles the high-level operation by the signalling messages and HSS.
- S-GW: Signaling Gateway performs mobility anchoring and forward data between PDN Gateway and Base Station.
- P-GW:Packet Data Network Gateway communicates with PDN’s employing interfaces. It performs operations like IP address allocation and packet filtering.
- PCRF: Policy and Charging Rule Function is accountable for controlling the flow-based charging operations in the Policy Control Enforcement Function (PCEF) and policy control decision-making.
2g 3g 4g Lte Comparison
Advantages of 3G
- It employs 2G frequency bands with bandwidths up to 230MHz are used to achieve global roaming and multi-services.
- Wideband radio channel to support high-speed services- Radio carrier channel uses bandwidth up to 20M which improvises chip rate and anti-multipath fading.
- In the broadband channel, the quality of business can be controlled by applying time multiplexing and code reuse. Different spreading factors, various rates need of different QOS can map into the broadband channel are selected to realise multi-service and multi-rate transmission.
- To improve the performance of the downlink transmission channel fast closed loop power control technology is applied.
- To adaptively adjust the power, lower the system self-interference and enhance receiver sensitivity and increase the system capacity, Adaptive antenna arrays are implemented to the 3G base station.
WCDMA, mainly comprised of the following two aspects i.e. Channel coding and power control. - Switching technology is required for communication of terminal and mobile networks when terminals aren’t steady and switching its position from the coverage of one base station to one of another base station.
Advantages of 4G
- Reduced delays for both connection establishment and transmission latency.
- Increased user Data Throughput.
- Increased cell edge bit rate.
- Minimized cost per bit employing enhanced spectral efficiency.
- Simplified network architecture.
- Seamless Mobility including between different Radio access technology.
- Reasonable power consumption for the mobile device.
- Minimises equipment cost as it abolishes need of costly frequency equaliser at receiver.
- It provides integrated security services.
Limitations of 3G
- The cost of cellular infrastructure, upgrading base stations is very high.
- Roaming and data/voice work collectively has not yet been implemented.
- Power utilisation is high.
- Needs short distance base stations and are expensive.
Limitations of 4G
- Location coordination and resource coordination to add new devices is not adequate.
- Limited voice calls and services can be handled a time.
- Being a concentrated data service, it requires broad bandwidth.
- It doesn’t provide good services in rural areas due to the requirement of the wireless network and 4G network isn’t expanded well in those areas.
Conclusion
4G technologies provides better services as compared to 3G technologies; in terms of data throughput, cell edge bit rate, cost, mobility, power consumption for mobile devices. However, there are some compatibility issues in 4G.